-
 Call Now ! +86 177 2978 0576
Call Now ! +86 177 2978 0576 -
 Email Now sale@kfqizhongji.com
Email Now sale@kfqizhongji.com


Introduction:
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, enabling precise and efficient production of complex parts. Two commonly used types of CNC machines are Vertical Machining Centers (VMC) and Horizontal Machining Centers (HMC). While both machines perform similar functions, there are significant differences in their design and applications. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between VMC and HMC in CNC machining.

• Structure and Workbench Difference Between VMC and HMC
The primary difference between VMC and HMC lies in their machine orientation. A VMC has a vertical spindle orientation, where the cutting tool moves vertically along the Z-axis.
On the other hand, an HMC features a horizontal spindle orientation, with the cutting tool moving horizontally along the X-axis. This distinction in machine orientation influences the types of machining operations each machine can perform efficiently.
• Difference in Workpiece Accessibility:
The orientation of the spindle in VMC and HMC affects the accessibility to the workpiece. The vertical machining center allow easy access to the top surface. This makes VMCs suitable for processing disk, sleeve, and plate parts. Because they require to be machined on the top surface, such as milling, drilling, and tapping.
In contrast, HMCs are ideal for machining operations that involve multiple sides of the workpiece, e.g. box and shell parts, for they have more than two sides or process holes and surfaces arranged radially around.
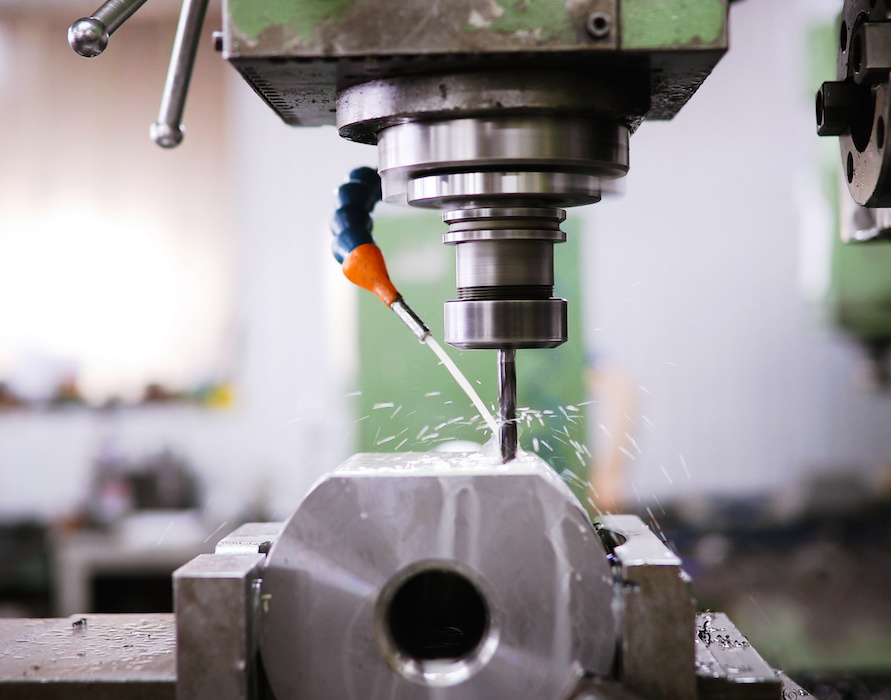

• Flexibility and Versatility:
VMCs are versatile and suitable for job shops and small-scale production. They excel in intricate detailing and precise contouring. HMCs are designed for high-volume production and heavy-duty tasks. Their horizontal spindle orientation enables them to perform face milling, deep-hole drilling, and large-scale production with enhanced chip evacuation.
• Floor Space and Footprint:
When choosing machines, consider the space required. VMCs are smaller and better for limited floor spaces. The compact design of VMCs also allows for easy integration into production lines or cells. HMCs are commonly used in dedicated production areas where high-volume production is the primary focus.
Conclusion:
In CNC machining, choosing between a VMC and an HMC depends on the specific requirements of the machining operation. VMCs offer versatility, precision, and suitability for smaller-scale production, while HMCs excel in high-volume production and multi-sided machining. Understanding the machining differences will help you in CNC machine that aligns with their production needs, ultimately optimizing efficiency and productivity in the machining process.