-
 Call Now ! +86 177 2978 0576
Call Now ! +86 177 2978 0576 -
 Email Now sale@kfqizhongji.com
Email Now sale@kfqizhongji.com


3-axis and 5-axis machining are two common methods of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining used for the manufacturing of parts and components.
Difference between 3-axis and 5-axis machining
The main difference between the two is the number of axes that the machine can move along. 3-axis machines move along the X, Y, and Z axes, while 5-axis machines can move along these three axes as well as two additional rotational axes, typically referred to as the A and B axes. The two additional rotational axes help achieve multi-sided processing, greatly improve the processing efficiency, reduce the program, especially the processing of cylindrical parts.
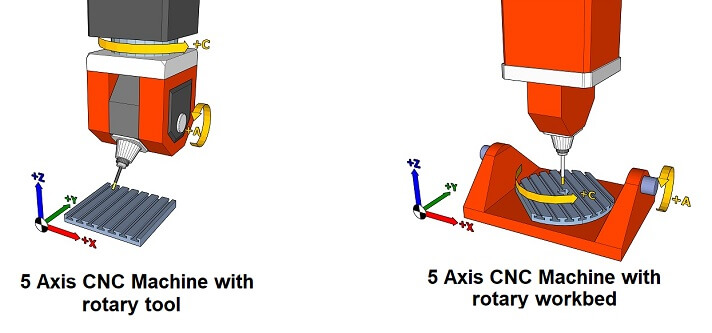
Application
3-Axis machining: Simple plate-part machining. Only process one side at a time.
4 Axis machining: Box-type parts machining. Intermittent cutting, continuous cutting, engraving curved surfaces, etc.
5 Axis machining: Complex shapes and high precision parts machining. Feature accuracy, increased productivity for medical, aerospace, military products, etc.
How to Choose
When selecting axes for CNC gantry machining, multiple factors like workpiece shape, precision, and budget must be considered.
That's because programming 3-axis machines is easier, which can save you money on costly expert programmers and operators. Plus, prep time is shorter with 3-axis machining.
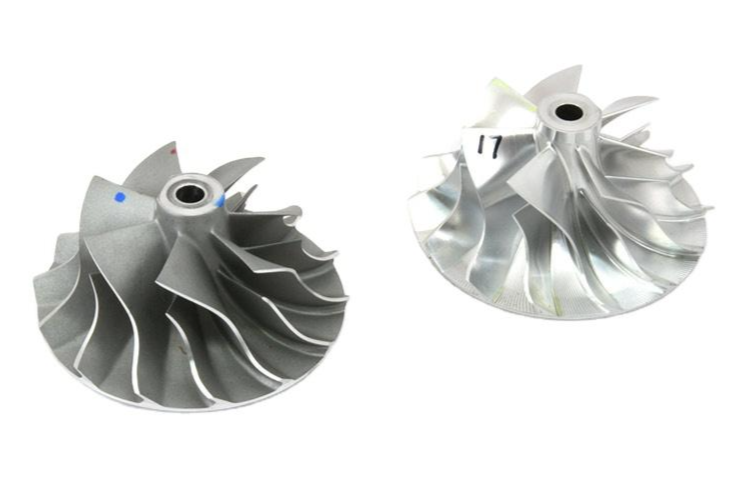

However, when you need to produce a deeper part or one with complex geometry, 5-axis machining benefits you greater accuracy and higher yields. For the 3-axis machining requires constant stopping and starting of the machine between each tool direction. So high speed is the primary advantage of 5-axis machining.
Our CNC machining experience is extensive, and we possess comprehensive machining equipment to control precision within ±50μm. Want to learn more about our CNC machining services? Contact us now!